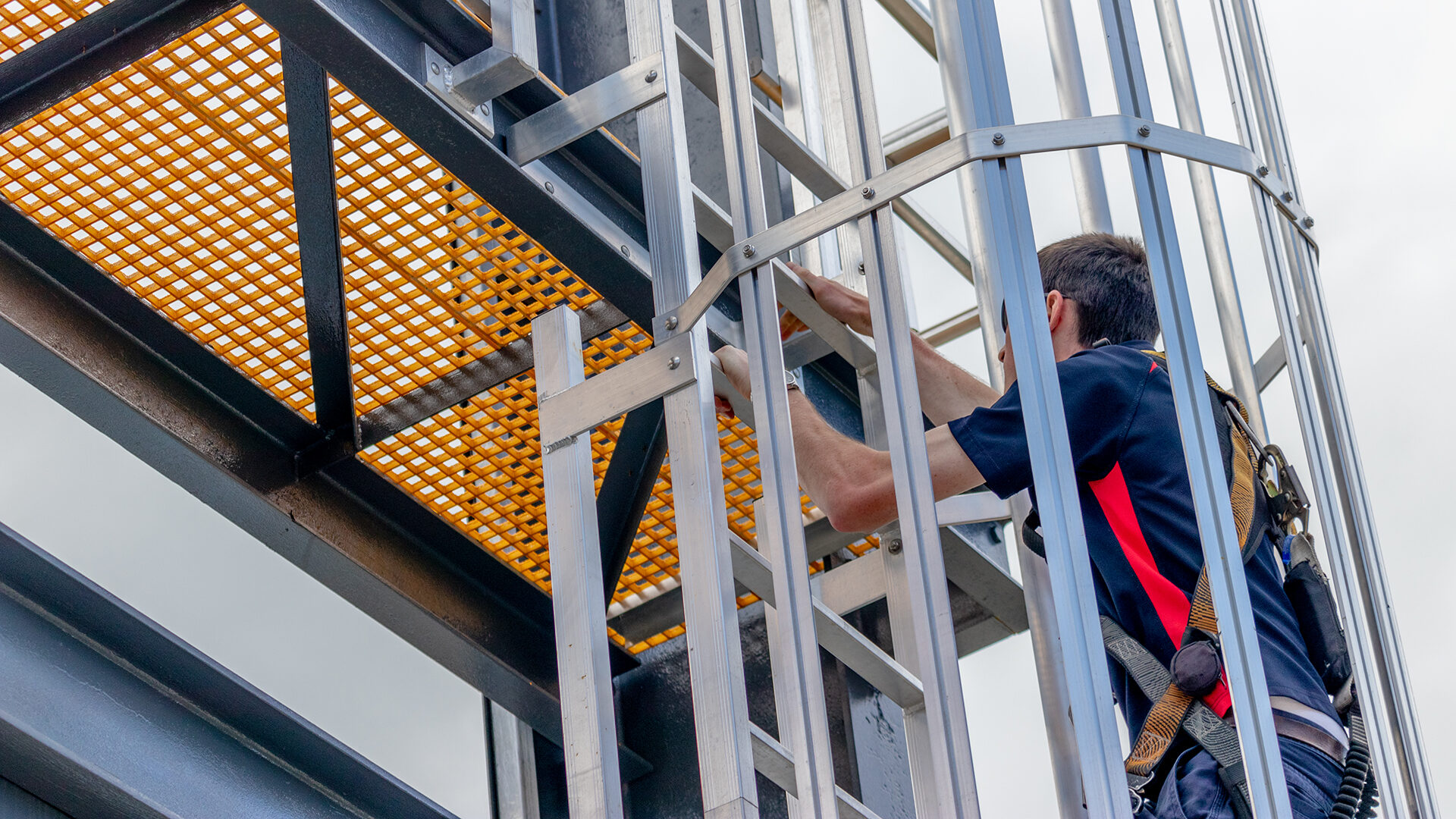
Fixed ladders are an excellent way of having a largely unobtrusive, permanent way to access a roof or other working at heights area. Here are five common problems our compliance team find with non-compliant fixed ladders.
As part of a height safety system’s regular inspection schedule, the technical team at Height Safety Engineers often finds itself looking at fixed ladders to see how they stack up against what it says in AS1657:2018.
What is AS1657:2018?
The full name of this standard is AS1657 Fixed platforms, walkways stairways and ladders – Design, construction, and installation. It is the Australian standard that sets out “requirements for the design, selection, construction and installation of fixed platforms, walkways, stairways and ladders that are intended to provide safe access to places used by operating, inspection maintenance and servicing personnel.”
It should be noted that AS1657 applies only to fixed, permanently installed ladders. It specifically sets out portable ladders are excluded and not covered. For portable ladders, you want AS1892 Portable ladders.
Issue one – Small or uneven landings
Fixed ladders are required to have a flat, even surface at both the top and bottom. This creates a stable platform from which a worker can enter or exit the ladder.
Clause 7.3.6 of the standard states that this area needs to be at least 600mm wide or if the ladder is wider than 600mm the landing should be made wider to match.
They are also required to have a depth of at least 900mm, measured from the face of the lowest rung or step of the ladder.
One common area where fixed ladders fail to adhere to this standard is when they are placed on pitched roofs. By their very nature, a pitched roof does not have a flat, even surface. The surface is sloped, often to a significant degree. An allowance in the standard is made for roofs with up to a 7-degree pitch. Those are considered flat for the purposes of ladder landings.
Any roof with a pitch greater than 7 degrees will require a purpose-built landing platform to be installed at the base of the ladder to be compliant with AS1657.
Issue two – Spacing from the bottom rung to the bottom platform
Spacing between the rungs on a ladder is to be even across its whole length, and this includes between the bottom rung and the landing platform at the base.
Clause7.4.3.4 of AS1657 requires that the spacing between the bottom rung of the ladder and the landing surface be between 90 and 100 per cent of the spacing between the rungs themselves.
For example, a ladder may have space between its rungs of 300mm. To be compliant with the standard, the spacing between the bottom rung and the landing must be between 270mm (90 per cent) and 300mm (100 per cent). Smaller, or larger, spacing renders the ladder non-compliant.
It is considered best practice to keep the spacing equal to that of the ladder itself, where possible.
Issue three – Clearances between ladder and wall or other structure (back of the ladder)
To safely ascend or descend a ladder, workers need to be able to gain a secure grip and foothold. To enable this, ladders are required to have a clearance between their rungs and the wall or structure to which they are attached.
In AS1657, Clause 7.4.5 describes the requirements for this clearance. From the back edge of the rungs to the structure, there should be a clearance of at least 200mm.
Issue four – Clearance between ladder and wall or other structure (front of the ladder)
There are also clearances that need to be adhered to. These allow a worker safe and clear passage up and down the ladder.
From the front edge of the rung, there should be at least 750mm clearance to allow space for the worker. From the centreline of the ladder to each side, the clearance should be at least 350mm.
In instances where the ladder is fitted with a ladder cage, additional considerations must be made.
Issue five – Slip-resistant rungs
Ensuring that the surface of the ladder is such that a worker can maintain a firm grip is essential to safety.
Clause 7.4.3.1 specifies that the surface of ladder rungs should be slip resistant. This can be achieved by having a corrugated, serrated, knurled, or dimpled surface. It can also be achieved through coating the ladder with a slip-resistant material.
Ladder inspections
Like all aspects of a safe access or fall protection system, fixed ladders should be inspected by a worker prior to use. Fixings and the physical state of the ladder should be checked to ensure it is safe to use.
As part of a height safety system, ladders should also be checked for compliance at least annually. Compliance inspections should be undertaken by an experienced height safety technician.
To find out more about compliance inspections and to understand the risks associated with non-compliant fixed ladders, talk to the team at HSE by calling 1300 884 978 or email enquiries@heightsafety.net.